BLUETOOTH BASED IEEE PROJECTS
EMBEDDED BLUETOOTH IEEE PROJECTS
1. A GSM mobile system to monitor brain function using a near-infrared light sensor
Year Of Publishing : 2008
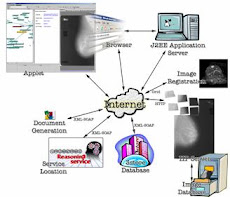
This paper presents a versatile mobile system to monitor oxygenated hemoglobin (HBO) and deoxygenated hemoglobin (HB) concentration changes in brain and tissues. The system uses global system for mobile communications (GSM) and Bluetooth networks to provide extended mobility. The system consists of three parts: a wireless near-infrared light sensor with Bluetooth support, a personal digital assistant (PDA) and a personal computer (PC). The sensor connects to the PDA using Bluetooth and the PDA connects to the PC in the lab using GSM and the Internet. The system packages the acquired data using multiple data communication protocols. It is a light-weight solution to monitor brain and tissues in real-life situations. The extended mobility was achieved by building software components in the PDA and the PC to provide the bridge between the Bluetooth sensor and the PC over GSM networks. The system was tested on humans and animals.
2. A gain scheduling strategy for the control and estimation of a remote robot via Internet
Year Of Publishing : 2008
In this article, a gain scheduling strategy for the controller of a remote robot based on Internet and Bluetooth networks is designed and implemented. The Internet communication is based on the master-slave structure, UDP protocol. The slave comprises a PC and a mobile robot, interconnected through the protocol Bluetooth. The master is a second PC which realizes the remote control, the design of which is based on a remote observer achieving a state prediction of the robot (slave), despite the variable communication delays, sampling and packets losses. The detected variable time-delays serve as the switching signals. The gain scheduling state feedback controller is based on Lyapunov-Krasovskii functional and the approach of LMI, which guarantee the uniform stabilization performance. 2008
3. Smart companion [contextual communication services]
Year Of Publishing : 2008
When today's connected 'nomads' move from place to place and try to interact with equipment in the vicinities they inhabit, e.g. hotspots in airports, ticket vending machine on train stations, appliances in the home, they need personalized help to ensure these interactions are effective. Operators can help these users by leveraging the network connectivity of the device these users carry. They can offer personalized help on such a device, which enables customers to communicate with surrounding equipment. On the one hand, the device has network connectivity, (3G, xDSL). On the other hand, it can interact with surrounding equipment using radio (WiFi, Bluetooth, etc). In this scenario, the user relies on this smart and secure device as if it is his/her companion. This is the idea behind the concept of a 'smart companion'. This is achievable today. Operators have entered into the service offering space in addition to their core network offerings (3G, xDSL etc). With the advantages of carrier grade infrastructure and connectivity with subscriber devices, operators are in the best position to host the preferences of network subscribers (language preference, appointments, etc.) in order to provision the users' requirements at any specific time or location. The paper discusses scenarios around such contextual services. It examines infrastructure requirements for provisioning of services to different user devices. The paper attempts to analyze the architecture, the current market situation and the challenges that have to be addressed for the successful roll out of such services. 2008
4. Open architecture for contactless smartcard-based portable electronic payment systems
Year Of Publishing : 2008
In this paper, we present a commercial-off-the-shelf (COTS) prototype design for a handheld, contactless, smartcard-based unit for the mass transit and regional rail systems. This project is an extension from two senior design project research efforts in the College of Engineering at Temple University which were focused on developing an open architecture design for the regional rails system of the South Eastern Pennsylvania Transportation Authority (SEPTA). The goal is to develop a non-proprietary and plug-in-and-play multi-modal transport payment (i.e. cash, credit card, passes, and more importantly the contactless smartcard) portable solution for the financially troubled public transit systems in the United States. Our proposed design utilizes an HP iPAQ hx2795 PDA (Personal Digital Assistant) with Bluetooth capability, an EXTECH S2500THS Bluetooth thermal printer/magnetic card reader, and an SDiD 1010 SD-interface contactless smartcard reader. As a result, the conductor will only need to carry the PDA device for ticket transactions; with the EXTECH s2500ths unit attached to the conductor’s belt. The system has been demonstrated with effective applicability, usability and durability for today’s transit systems. 2008
5. Optimized Autonomous Space In-situ Sensor-Web for Volcano Monitoring
Year Of Publishing : 2008
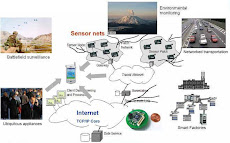
In response to NASA's announced requirement for Earth hazard monitoring sensor-web technology, a multidisciplinary team involving sensor-network experts (Washington State University), space scientists (JPL), and earth scientists (USGS cascade volcano observatory (CVO)), is developing a prototype dynamic and scaleable hazard monitoring sensor-web and applying it to volcano monitoring. The combined optimized autonomous space - in-situ sensor-web (OASIS) will have two-way communication capability between ground and space assets, use both space and ground data for optimal allocation of limited power and bandwidth resources on the ground, and use smart management of competing demands for limited space assets. It will also enable scalability and seamless infusion of future space and in-situ assets into the sensor-web. The prototype will be focused on volcano hazard monitoring at Mount St. Helens, which has been active since October 2004. The system is designed to be flexible and easily configurable for many other applications as well. The primary goals of the project are: 1) integrating complementary space (i.e., Earth observing one (EO-1) satellite) and in-situ (ground-based) elements into an interactive, autonomous sensor-web; 2) advancing sensor-web power and communication resource management technology; and 3) enabling scalability for seamless infusion of future space and in-situ assets into the sensor-web. To meet these goals, we are developing: 1) a test-bed in-situ array with smart sensor nodes capable of making autonomous data acquisition decisions; 2) efficient self-organization algorithm of sensor-web topology to support efficient data communication and command control; 3) smart bandwidth allocation algorithms in which sensor nodes autonomously determine packet priorities based on mission needs and local bandwidth information in real-time; and 4) remote network management and reprogramming tools. The space and in-situ control components of the system will be in- tegrated such that each element is capable of autonomously tasking the other. Sensor-Web data acquisition and dissemination will be accomplished through the use of the open geospatial consortium sensor-web enablement protocols. The three-year project will demonstrate end-to-end system performance with the in-situ test-bed at Mount St. Helens and NASA's EO-1 platform. 2008
6. A mobile web grid based physiological signal monitoring system
Year Of Publishing : 2008
Monitoring of physiological signals of disaster affected patients inherit several challenges. First of all, the care providers of a disaster zone are susceptible to health hazards for themselves. Fast and easy transportation of monitoring equipments is crucial for survival of the injured. Moreover, Enormous physiological data transmission from the disaster zone to the medical server needs to be regulated to prevent network congestion. In this paper, we are proposing a mobile grid based health content delivery service, which can be useful for vital signal monitoring from a remote location. The proposed system is specifically designed for monitoring of a group that is very much mobile and dynamic in nature. Therefore, during a catastrophic event like earth quake, flood, cyclone the whole system can be transported with minimal mobility to the disaster affected patients. Minimally trained people are capable of installing the system within the disaster affected area entirely in ad-hoc manner. Medical experts can monitor the group from a safe location and provide specialist advice for the early recovery of the affected patients. To deal with network congestion, local intelligence is applied within the mobile patient monitoring system. Therefore, only medically urgent information is transmitted to the hospital server or central server. Application of grid network provides additional computational power to analyze raw physiological signal to identify possible health hazards for the monitored patients. In addition, the proposed mobile grid provides load sharing and redundancy of patient data, which are of prime importance for a disaster zone. 2008
7. Real-time Bluetooth communication system for control of a mobile robot
Year Of Publishing : 2008
This paper presents a measurement platform of Bluetooth asynchronous links in order to obtain the intrinsic temporal constraints of this network and communication protocol. These temporal measurements are necessary for the application the authors wish to implement for mobile robot control through a Bluetooth communication link. The platform, as well as the measurement protocol, which is based on real-time communication operating systems, is presented. An application of radio and temporal data processing allowing a real-time evaluation of the global behaviour of the communicating system has been developed. 2008
8. Mobile computing for indoor wayfinding based on bluetooth sensors for individuals with cognitive impairments
Year Of Publishing : 2008
A novel wayfinding system is presented with an aim to increase workplace and life independence for cognitive-impaired patients such as people with traumatic brain injury, cerebral palsy, mental retardation, schizophrenia, and Alzheimerpsilas disease. According to psychological model of spatial navigation and the requirements of rehabilitation professionals, PDAs prompting with spatial photos at the right time and place can assist cognitively-impaired persons with navigating indoors or on the road. To do so, Bluetooth sensors which can be imagined as a new traffic sign system, are posted to selected positions on routes. The navigational photos are served on demand to the user who uses the built-in Bluetooth to scan the Bluetooth sensors. A prototype is designed and tested on a university campus. The experimental results show the computer-human interface is friendly and the capabilities of wayfinding are reliable.
9. Bluetooth/GMRS Car Security System with a Randomly Located Movement Detect Device
Year Of Publishing : 2006
A car security system that links the user, a starter disable unit and a randomly located device is presented. The last one actuates as a movement detector, and the user can hide it anywhere inside the vehicle, which gives a strong level of security since there is no physical attachment to the car. A prototype has been constructed, using Bluetooth between the non-fixed device and the starter disable unit; the system sends a warning message to the user if any movement is detected via general mobile radio service (GMRS). Test results and some future improvements are commented at the end of this paper 2006
8. Bluetooth Based Wireless Remote Device Controlling and Data Acquisition
Year Of Publishing : 2006
IrDA has been used for controlling devices and machines wirelessly at home, office and industry so far. The most disadvantageous part in this case is the line of sight and only point to point communication where Bluetooth had opened the door far wider to these points. Because it doesn’t have line of sight problem and it is capable of both point to point and point to multipoint wireless communication. Moreover, attachment facility of low cost, commercial microcontroller as the host controller interface had facilitated straight and effective development. This paper will present an application model for Bluetooth wireless remote controller mostly suitable for short range uses. The contribution is the developed system where the design has been simulated with real-time implementation to test the stability of the overall system. The system is built up of generally available Bluetooth components. Performance analysis has been carried out to make sure of keeping the operational flexibility to be within acceptable range. The laboratory prototype came up with the experimentation, covers most of the general uses and sophisticated digital and analog devices ones as well. 2006
9. Bluetooth Remote Control
Year Of Publishing : 2006
The aim of this paper is to present our "Bluetooth Remote Control" Application which is based on client-server application. The client application runs on mobile phone and the server application runs on PC using J2ME and J2SE respectively. This application can be used to control PCs via mobile phone. For example it can open the Internet Explorer, Media player, Power Point, MSN messenger and control the mouse. The application can be also used to control electrical devices using the parallel (LPT) port of PC. 2006
10 .Bluetooth Based Wireless Remote Device Controlling and Data Acquisition
year Of Publishing 2006
IrDA has been used for controlling devices and machines wirelessly at home, office and industry so far. The most disadvantageous part in this case is the line of sight and only point to point communication where Bluetooth had opened the door far wider to these points. Because it doesn’t have line of sight problem and it is capable of both point to point and point to multipoint wireless communication. Moreover, attachment facility of low cost, commercial microcontroller as the host controller interface had facilitated straight and effective development. This paper will present an application model for Bluetooth wireless remote controller mostly suitable for short range uses. The contribution is the developed system where the design has been simulated with real-time implementation to test the stability of the overall system. The system is built up of generally available Bluetooth components. Performance analysis has been carried out to make sure of keeping the operational flexibility to be within acceptable range. The laboratory prototype came up with the experimentation, covers most of the general uses and sophisticated digital and analog devices ones as well.
11 . Networked Remote Meter-Reading System Based on Wireless Communication Technology
A networked remote meter-reading system based on Bluetooth wireless communication technology and GSM is presented in this paper. The remote meter-reading system employs distributed structure, which consists of measure meters, sensors, intelligent terminals, management centre and wireless communication network. The intelligent terminal which designed based on embedded system and Bluetooth technology is used to realize acquisition information submitted from meters and sensors control the energy-consuming devices moreover in residence. The message communicated between the intelligent terminal and management centre by dint of GSM network. The structure and function of this meter-reading system are described and the system's hardware and software detailed. The meter-reading task can be finished at the management centre of residence area by using this system. The system has many significant excellences, such as wireless, low-workload, great quantity of data transmission, high-veracity and low-expenses. The using of embedded system improves the stability of wireless data transmission. The remote meter-reading system which can be propitious to administer energy-source and continuous development have abroad application foreground 2006
12. Application of Bluetooth technology in ambulatory wireless medical monitoring
Year Of Publishing : 2004
Traditional cable medical monitoring has many shortcomings. Bluetooth is a good solution to resolve those problems is discussed. Then a Bluetooth holter is taken as an example, some important design considerations and experiences are introduced. This example can easily be transplanted to other monitoring and recording fields.
13. Coupling between Bluetooth modules inside a passenger car
Year Of Publishing : 2004
There are many potential opportunities for exploiting Bluetooth links in vehicle applications, including communications both within the vehicle and between the vehicle and the external environment. However, there is little practical experience of determining propagation characteristics within vehicles at these frequencies. This paper reports on initial studies to investigate these issues, for in-vehicle communications in particular. 2004
14. Remote-controlled home automation system via Bluetooth home network
Year Of Publishing : 2003
The idea of a home automation has been an important issue in many publications and home appliances companies. Home automation is a house or living environment that contains the technology to allow devices and systems to be controlled automatically. Remote and local control is useful to keep home comfortable and to support the elderly and the disabled people. In this paper, we discuss possible developments of Bluetooth wireless technologies and describe the hardware for devices and software for the considerations of a home automation system. Finally, we have validated the testbed by simulating in the Bluetooth home network. 2003
15. Usage of BluetoothTM in wireless sensors for tele-healthcare
Year Of Publishing : 2003
The small size and low power consumption of the radio module, use of spread spectrum, and the design for shortrange transmission make Bluetooth™ an attractive option in medical sensors. Since Bluetooth™ will continue to be a feature found in many devices it is worthwhile to investigate in its use in wireless medical sensors for home-based tele-healthcare. A wireless stethoscope has been implemented using Bluetooth™ and PCM encoding. Preliminary results show that it is a feasible solution for transmission of heart and lung sounds. Design of a Bluetooth™ wireless ECG is also proposed. 2002
16. Remote system for patient monitoring using Bluetooth
Year Of Publishing : 2003
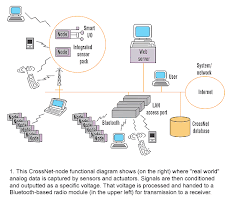
The aim of this study is to design and develop a low-power wireless A/D-converter that should be easy to integrate with other technologies or infrastructures at a low cost. This transmitting unit should be able to replace many of the signal wires between biomedical sensors connecting the patient and the sampling unit or supervision equipment. The model of today is an embedded hardware solution with two processors (FPGA and Bluetooth). A twelve bit ADC with a 1 kHz-sampling rate then converts an analogue signal that simulates an ECG-signal with typical frequencies. The communication between the ADC and Bluetooth™ is serial and controlled by the FPGA. The remote PC runs a simple software that controls the Bluetooth™ and processes the received data. The results indicate that it is possible to continuously transmit an ECG-signal without losing data.
17. Using Bluetooth transceivers in mobile robot
Year Of Publishing : 2003
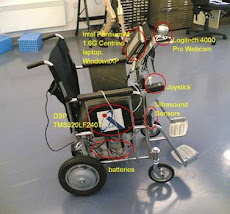
This work explores the implementation of Bluetooth technology in mobile robots. The mobile robot has the capability to move around autonomously using a complicated and powerful algorithm. The algorithms are stored in a PC that acts as a master cum server. All sensor readings from the mobile robot are transmitted to the master and processed. Then, a command or instruction for further action is transmitted from the server to the mobile robot in a bidirectional full duplex communication mode. Hence, the main "brain" is in the server instead of the mobile robot. This paper focuses on the interfacing between the Bluetooth transceiver and the Handy Board MC68HC11 micro-controller of the mobile robot. For a common case, a receiver and transmitter are needed for each device (robot and control unit), but with Bluetooth technology, only two Bluetooth transceivers are needed to achieve the full duplex connection.
18. Bluetooth enabled mobile robot
Year Of Publishing : 2002
This paper explores the implementation of Bluetooth technology in mobile robots, to give robots the capability to move around autonomously with more complicated and powerful algorithm. The mobile robot will act based on algorithm stored in the server. All the sensor readings from the robot will be transmitted to the server and processed. Then, command/instruction for next action is transmitted from the server to the mobile robot. Hence, the main "brain" is the server instead of on the mobile robot. This paper will focus on the protocol in using Bluetooth for controlling a mobile robot using the Handy Board MC68HC11 micro controller.